Adding a Project#
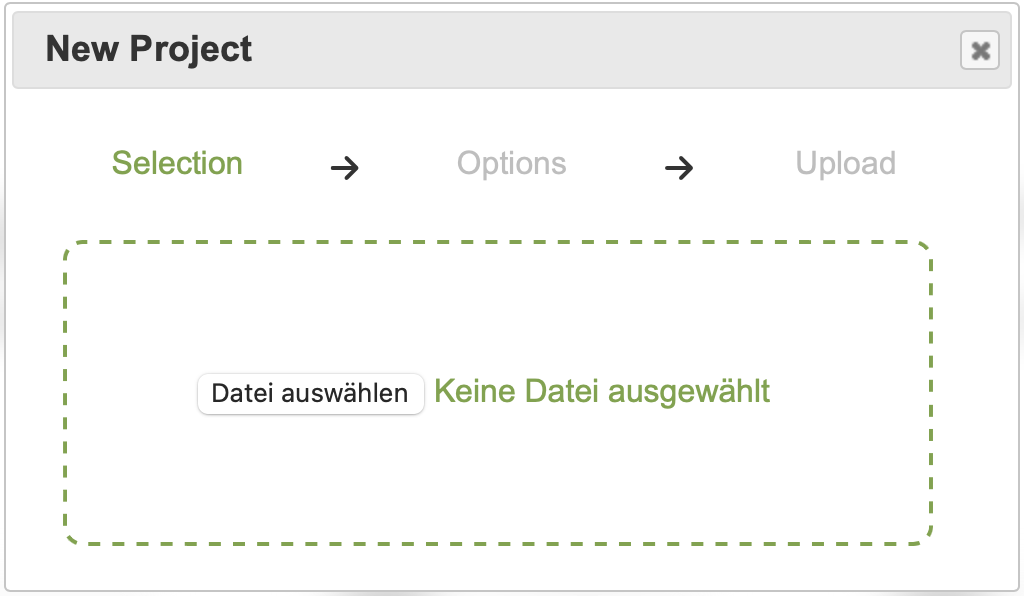
To add a new project, click on the first tile in the project dashboard. This will open the project creation dialog.
Currently, Forester is only able to illustrate classification trees that have been generated in other environments. Forester natively supports outputs from the two common environments Matlab and R. For Matlab the function fitctree is supported, while for R it is rpart.
Matlab’s fitctree#
To illustrate a Matlab decision tree with Forester, you need to train your model using fitctree. If you don’t know how to do this, you can read up on the process here.
There is sadly no open-source software that reads Matlab files. It is therefore not possible to directly upload .m files and you need to use a small workaround. All you need to do is to export the model in a json format. This can be done by using the native Matlab function jsonencode more on which you can read here.
As an example, the following script illustrates how a Matlab model for Fisher’s Iris data can be trained and exported for usage in Forester:
% load Fisher's Iris data
load fisheriris;
iris = array2table(meas, 'VariableNames',{'Sepal.Length', 'Sepal.Width', 'Petal.Length', 'Petal.Width'});
iris.Species = single(categorical(string(species)))
% train model
tree = fitctree(iris, 'Species');
% convert to json
json = jsonencode(tree)
% save json
file = fopen('iris.json','wt');
fprintf(file, json);
fclose(file)
You can now upload the file iris.json. After that, Forester asks you to give it some more information on the project.
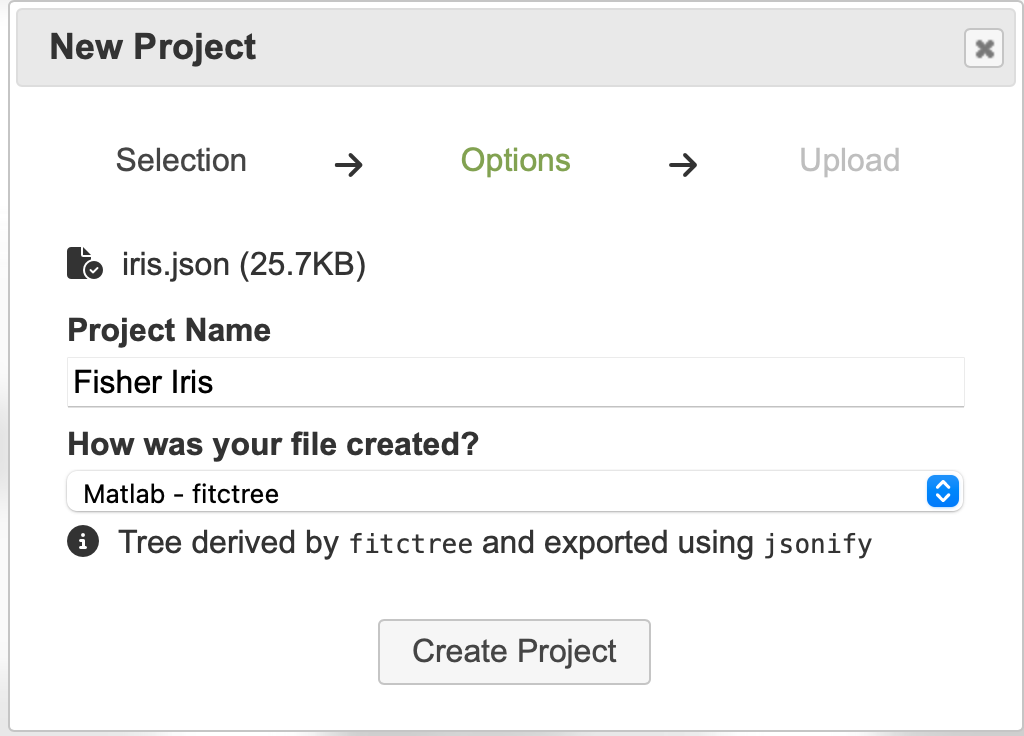
You can set the name of the project in the corresponding field. Because Forester accepts multiple different json formats, you need to specify that this file originates from Matlab by selecting answering the question How was your file created? with “Matlab - fitctree”.
After you clicked Create Project the server parses the file and creates a new project for you. When no error occurs, the dialog is closed automatically und you will find the new project in the dashboard. When an error occurs, it is displayed in the dialog.
Upload a File
Fill in the required fields
You should not see this error
All done! You are now ready to continue working on your project in the editor.
R’s rpart#
For models trained in R, the process is a bit more straightforward. After training the model with rpart, you can simply export the result using the native function save. The following section illustrates, how a model can be trained for Fisher’s Iris data and exported for usage in Forester.
require(datasets)
require(rpart)
# load the data
iris = datasets::iris
# train the model
tree = rpart(as.factor(iris$Species) ~ ., data=iris)
# name is irrelevant, but only save the
# model and not other data in the environment
save(tree, file="iris")
You should now have a file called iris.RData that you can upload to the project creation dialog. In the project options you can again assign a name to the project. The question How was you file created? should default to “R - rpart”, as Forester only supports this routine at the moment. Nonetheless, check that this field is set correctly.
Important
When you want to create projects from .RData files you need to have R installed. Otherwise, Forester is not able to parse the .RData file.
After you clicked Create Project the server parses the file and creates a new project for you. When no error occurs, the dialog is closed automatically und you will find the new project in the dashboard. When an error occurs, it is displayed in the dialog.
All done! You are now ready to continue working on your project in the editor.